Using Bloom’s Cognitive Taxonomy to Develop Learning Objectives
Description
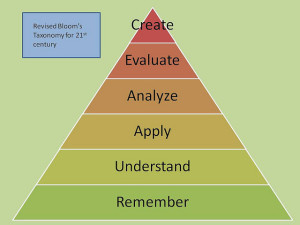
Since it was published in 1956, teachers at all levels of education have used Bloom’s Taxonomy as an aid to develop measurable learning objectives for students. In its latest version, Bloom’s Taxonomy consists of six major categories, listed here from higher order to lower order: Create, Evaluate, Analyze, Apply, Understand, and Remember. Each level includes specific verbs that can aid in constructing learning objectives. Effective teaching aims to guide students from remembering toward creation.
Purpose
Use Bloom’s Taxonomy to create higher order learning objectives that are specific, measurable, and performance-based. Clear and organized objectives help teachers to:
- deliver appropriate instruction
- design valid assessments
- align instruction/assessment with the objectives.
Bloom’s Cognitive Taxonomy Hierarchy (2001):
6. Create: Generating, Planning, Producing
Related verbs: choose, support, relate, determine, defend, judge, grade, compare, contrast, argue, justify, support, convince, select, evaluate
5. Evaluate:Checking, Critiquing
Related verbs: design, formulate, build, invent, create, compose, generate, derive, modify, develop
4. Analyze: Differentiating, Organizing, Attributing
Related verbs: classify, outline, break down, categorize, analyze, diagram, illustrate
3. Apply: Executing, Implementing
Related verbs: calculate, predict, apply, solve, illustrate, use, demonstrate, determine, model
2. Understand: Interpreting, Exemplifying, Classifying, Summarizing, Inferring, Comparing, Explaining
Related verbs: describe, explain, paraphrase, restate, give original examples of, summarize, interpret, discuss
1. Remember: Recognizing, Recalling
Related verbs: list, recite, define, name, match, quote, recall, identify, label, recognize
https://www.flickr.com/photos/langwitches/3213256269/
Considerations
- Identifying learning objectives requires careful, thorough analysis of lectures, lessons, and activities.
Level
- Beginner
Resources:
Marzano, Robert J., and John S. Kendall. Designing & Assessing Educational Objectives: Applying the New Taxonomy. Thousand Oaks: Corwin, 2008. Print.
Task-Oriented Question Construction Wheel Based on Bloom’s Taxonomy ©2004 St. Edward’s University Center for Teaching Excellence.
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy from UNC Charlotte Center for Teaching and Learning
Bloom’s Taxonomy from Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching
Anderson, Lorin W., and David R. Krathwohl. A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. New York: Longman, 2001. Print.

