Digital Image Compression
Description:
Image compression technologies work to minimize the file size of digital images. The three common compression formats used for images on the web are JPEG, GIF and PNG.
Purpose:
Finding the best fit compression format for an image yields the highest image quality with the smallest file size—smaller file sizes will make projects load faster.
Procedure:
- Open the image in the image editing tool of your choice.
- Save a copy of your file using the best compression format for you image and needs:
- JPEG: best option if you don’t need transparency or animation.
- GIF: used for small images or illustrative images with blocks of the same color. Supports animation and transparency.
- PNG: good for images with uniformly colored areas. Uses lossless compression which results in a higher quality image, but files sizes are larger. Supports transparency.
- Tune compression settings to the lowest acceptable quality level with optimal file size reduction.
Tools for working with digital images:
- Desktop apps: Photoshop, Gimp, or iPhoto.
- Web-based/mobile processing: Pixlr.
- Compressors: gifsicle, jpegtran, optipng, pngquant.
Considerations:
- Keep copies of your original uncompressed images.
- Only compress your images once. If you need to edit an image do so on the original. Compressing an already compressed image further reduces quality.
- If you are working on an online project, try the “Save for the Web” or “Optimize for the Web” option found in most image editing tools.
Level:
Beginner
Resources:
- http://www.html5rocks.com/en/tutorials/speed/img-compression/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image_file_formats
- https://developers.google.com/web/fundamentals/performance/optimizing-content-efficiency/image-optimization?hl=en
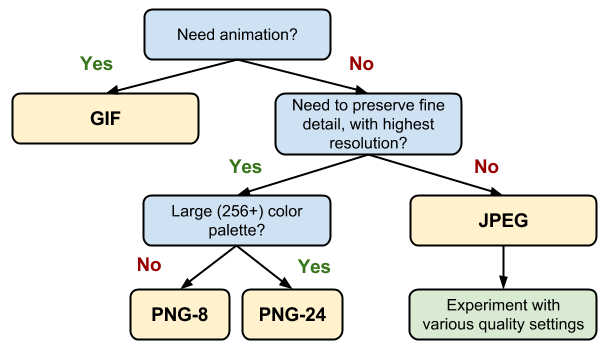
Image credit: https://developers.google.com/web/fundamentals/performance/optimizing-content-efficiency/image-optimization?hl=en